All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Gasotransmitters in Plants: Mechanisms of Participation in Adaptive Responses
Abstract
Plant adaptive responses to environmental stresses occur with the participation of plant hormones and a network of signaling mediators. Among these, a growing attention has been paid over the recent years to gasotransmitters (GT). This term is used to define small gaseous molecules synthesized by living organisms that perform signaling functions. The main GT in plants are nitrogen monoxide (NO), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen sulfide (H2S). The mechanisms of GT participation in the processes of plant adaptation to unfavorable environmental conditions have not yet been studied enough, which limits the use of GT in crop production. This review summarizes the latest data on GT synthesis in plants, the ability of GT to induce post-translational protein modifications in plants and to functionally interact with each other and with other signaling mediators. Particular attention is paid to the participation of GT in the regulation of antioxidant system, the state of cytoskeleton, and stomatal reactions of plants. These effects are important for stimulation by gasotransmitters the adaptation of plants to extreme temperatures, drought, and salinity. The possibilities of using GT donors in crop production were also considered.
1. INTRODUCTION
Abiotic stresses are the main constraints on plant growth and development [1]. According to predictive climatic models, by the end of the 21st century, the temperature on the planet will have increased by 3.7 ± 0.7°С [2]. A rise in the global temperature by a single degree leads to a decrease in global yields of major crops by 3-8% [3]. An equally serious climate threat nowadays is the change in the amount and distribution pattern of precipitation over time and space [4]. It is predicted that by the last third of this century, soil moisture in many parts of the world will have reduced compared to the beginning of the 21st century, against significant disproportions in the quantity and intensity of rainfalls between various regions. Drought is considered one of the major environmental factors inhibiting plant growth and productivity [5]. Plants are usually negatively affected by high temperatures, excessive illumination, soil salinity, and other stresses [6].
The main approaches to improve the resistance of cultivated plants towards unfavourable external conditions are based on the methods of traditional breeding and genetic engineering, which are used to transfer certain genes of interest, providing such resistance. Additionally, biologically active substances and other means are used to activate the physiological mechanisms of resistance. Plants develop adaptive responses to stresses with the participation of plant hormones and a range of signaling mediators, among which calcium and active oxygen compounds play a special role [7, 8]. Gasotransmitters are also considered presently as important signaling mediators [9-12]. The most recent research findings indicate that gasotransmitters possess a large potential as amplifiers of plant adaptive responses that is still almost not realized in crop production.
The term “gasotransmitters” (GT) is used to define small gaseous molecules synthesized by living organisms that perform signaling functions. Such molecules are able to pass through cellular membranes; they function independently of specific receptors and can be generated by enzymes. Besides, they react with specific cellular target components and can closely interact with other signaling mediators [13]. It is also believed that the exogenous effect of GT on living organisms should mimic their function. The main GT in plants are nitrogen monoxide (NO), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) [11, 12]. Recently, gaseous hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), and gaseous phytohormone ethylene (C2H4) have also been considered as GT. At the same time, the features of ethylene action are not fully consistent with the general GT concepts, while physiological functions of endogenous hydrogen and methane, and the mechanisms of their synthesis in plants, have not been properly studied yet [12, 14, 15]. Additionally, to the above, GT plays a role in the regulation of cell cycle in plants, formation and functioning of the cytoskeleton, seed germination, de-etiolation, and rhizogenesis [16-19], as well as in aging, interaction of plants with symbionts [20] and pathogens [21-23]. Furthermore, GT plays a particularly important role in plant adaptation to the unfavorable environmental conditions [11, 12, 24].
It has been shown that the GT generation by plants is enhanced in response to the abiotic stresses of various nature [11, 12, 25]. In recent years, the possibilities of the practical application of GT donors to increase plant resistance in crop production and crop storage technologies have been actively explored [26-29]. At the same time, the mechanisms of GT induction of stress-protective systems in plants remain largely unclear. At present, the overall awareness of the GT targets is rather fragmented, albeit it is dynamically accumulating [30, 31]. GT keeps complex functional interconnections with each other and other actors in the signaling network of plant cells and with plant hormones [32, 33]. Active research into the mechanisms of such interaction has only been carried out in the last decade and a half. The purpose of this review is to analyze the latest information on the phenomenology and mechanisms of stress-protective action of key GT (NO, CO and H2S) on plants, and the feasibility of their practical use in agrobiotechnology.
2. GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT GASOTRANSMITTERS IN PLANTS AND THEIR SYNTHESIS UNDER STRESS CONDITIONS
2.1. Nitric Oxide
Currently, NO is considered one of the most important components of the signaling network of plant and animal cells [34]. Nitric oxide-induced signaling occurs through the generation of a series of molecules called reactive nitrogen species (RNS) [35]. These include peroxynitrite (ONOO–), •NO2, and S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) [36]. RNS serve as markers of nitrosative stress in plants. High concentrations of nitric oxide are toxic for plants in connection with its capacity both to interact with biomacromolecules, and to undergo reactions, leading to the ROS formation [27]. Overproduction of RNS, often coupled ROS, may be responsible for the development of cell lesions and death [35].
NO in plants is generated in either reduction or oxidative pathways [37]. The reduction pathway involves the use of nitrate or nitrite as substrates in the reactions catalyzed by nitrate reductase, plasma membrane-bound nitrite-NO reductase, and xanthine oxidoreductase localized in peroxisomes [38, 39] (Fig. 1A). It is the nitrate reductase-dependent pathway that is assumed to be the main pathway of NO synthesis [40]. This pathway is involved in plants adaptation to stresses, such as low temperatures, dehydration, and hypoxia [41]. Nitrate reductase activity, which determines the synthesis of nitric oxide in plant cells, was detected mainly in the cytosol [39].
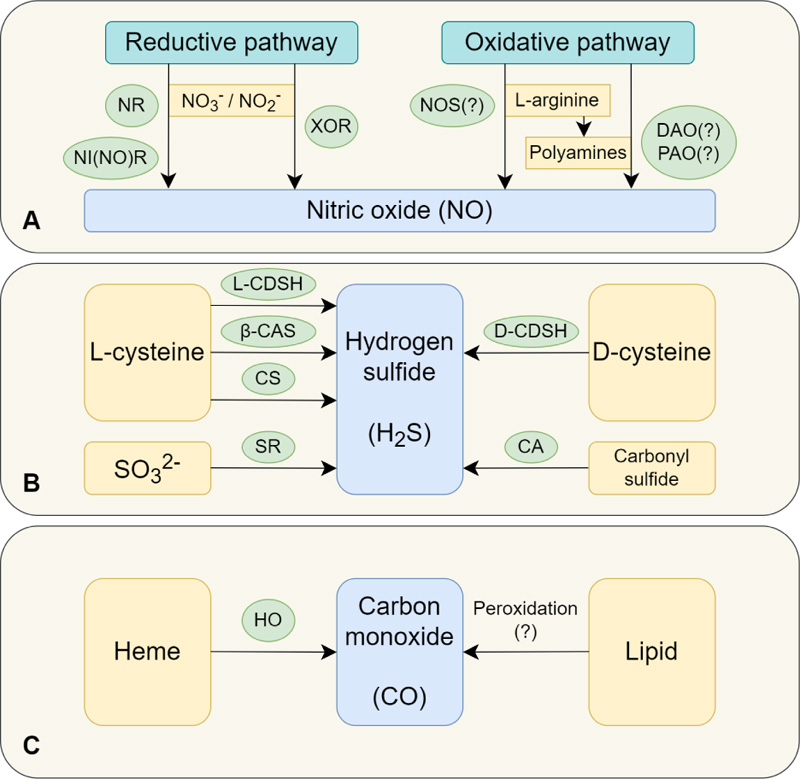
The mechanisms of nitric oxide synthesis via the oxidative (L-arginine-dependent) pathway remain a matter of debate. It is assumed that this pathway of NO synthesis may be similar to that in animal cells. However, to date, homologs of animal NO synthase have been identified only in green algae (Ostreococcus tauri and O. lucimarinus), but not in higher plants [40, 42]. There is an assumption that the gene for NO synthase (NOS) got lost during the evolution of plants [41]. At the same time, it is likely that peroxisomes in the higher plants contain proteins other than NOS, but capable of generating NO using L-arginine as a substrate. This reaction, similar to that catalyzed by animal NO synthase, can occur in the presence of NADPH, FMN, FAD, calmodulin, and calcium ions [33, 37, 43]. It has been shown that the inhibitor of mammalian NO synthase L-NAME (NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester) inhibits primary root growth, induces the differentiation processes in Arabidopsis roots, and reorganizes cortical microtubules in epidermal root cells, suggesting the importance of L-arginine-dependent pathways of NO synthesis in plants [44]. Such a reaction can possibly take place in chloroplasts, mitochondria, and peroxisomes [39]. Recently, not only L-arginine but also polyamines and hydroxylamine, have been considered as the main substrates for the NO formation via the oxidative pathway [45]. It is assumed that these transformations can be catalyzed by di- and polyamine oxidases localized predominantly in the cell walls [46].
The content of nitric oxide in plant cells depends not only on its synthesis but also on the functioning of the mechanisms of its disposal [47]. The most significant reservoir of NO is S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), which results from the reaction between nitric oxide and glutathione (GSH). The content of GSNO is regulated by S-nitrosoglutathione reductase, which reduces GSNO to glutathione sulfinamide (GS(O)NH2) using NADH [48]. Another effective way to dispose of the excessive nitric oxide is via its binding with non-symbiotic forms of hemoglobin with subsequent conversion into nitrite [47].
Growth of the nitric oxide levels in plants was observed in response to stresses of a very different nature. For instance, an increase in the NO content in roots and leaves of plants was detected under the conditions of moderate osmotic stress [49, 50]. Also, the content of endogenous NO in tobacco plants was reported to raise up in response to salt stress. This effect was manifested against the background increase in the activity of nitrate reductase and arginine synthase [51]. Besides, an increase in the NO content in organs of plants of different species was shown during hypothermia. This effect was caused by both short-term (1-4 h) and long-term (7-14 days) exposure of plants to low temperatures [52-55].
Furthermore, the literature describes an increase in NO content in plants of various species in response to high temperatures [56-58]. This effect manifests itself transiently and, probably, depends on the reactions of both the reductive and oxidative pathways of NO synthesis (Karpets et al., 2015). At a number of objects, nitrogen oxide content was recorded to increase in response to the action of heavy metals, aluminum, and arsenic [59-62].
2.2. Hydrogen Sulfide
Until the 1990s, hydrogen sulfide in the physiology and biochemistry of animals and plants was considered mainly as a toxicant. Later, experimental data began to accumulate, indicating a possible signaling role of hydrogen sulfide in plant cells [63]. Currently, data has been obtained about its close functional relationships with other known signaling mediators (in particular, with calcium ions, nitrogen monoxide, and ROS), as well as with a number of plant hormones [64, 65]. In this regard, hydrogen sulfide is considered as an agent participating in the regulation of numerous functions of plants, in particular, the processes of growth, ripening and aging of fruits, adaptation to stresses of a very different nature [65-68]. Today, hydrogen sulfide is considered a trigger for the cross-adaptation of plants [69].
Hydrogen sulfide in plants can be synthesized by at least six enzymes. One of the main pathways for the synthesis of hydrogen sulfide in plants is the conversion of L-cysteine into pyruvate with the release of hydrogen sulfide and ammonium (Fig. 1B) [70]. This reaction is catalyzed by L-cysteine desulfhydrase, which is probably localized in cytoplasm, plastids, and mitochondria [63, 71]. It is also possible to form hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine under the action of D-cysteine desulfhydrase in the cytoplasm [71, 72]. In addition, hydrogen sulfide can be synthesized by the reduction of sulfite with the involvement of sulfite reductase [63]. In this case, reduced ferredoxin is used as a sulfur reducer.
The H2S formation in plants can also occur with the participation of β-cyanoalanine synthase [64]. This enzyme is localized in mitochondria and catalyzes the condensation reaction of L-cysteine and cyanide with the release of hydrogen sulfide [73]. Its main function is believed to be related to the control of toxic cyanide levels. Cysteine synthase, localized in cytosol, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, can also contribute to the H2S synthesis (Fig. 1B). It catalyzes the reversible reaction between L-cysteine and acetate to form O-acetyl-L-serine and H2S [73, 74]. In addition, hydrogen sulfide can release during the decomposition of carbonyl sulfide using carbonic anhydrase in chloroplasts and cytoplasm (Fig. 1B) [75].
We are not aware of any information on non-enzymatic pathways for the synthesis of H2S in plants. At the same time, there is evidence that a small amount of hydrogen sulfide can be formed in mammalian cells without the participation of enzymes.For example, glucose could react with methionine, homocysteine or cysteine to produce gaseous sulfur compounds, including hydrogen sulfide [72].
Along with enzymatic systems for the synthesis of hydrogen sulfide, plants contain an enzyme that ensures its degradation – O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase [76]. An increase in the endogenous content of hydrogen sulfide in plants was found under stresses of various nature. In particular, under the low temperature, a transient increase in the endogenous H2S content and an increase in the expression of genes of the key enzymes of its synthesis, L-/D-cysteine desulfhydrases, were shown in plants of various species [77-79]. A transient increase in the content of hydrogen sulfide was also found in response to hyperthermia [76, 80]. Activation of the expression of L-and D-cysteine desulfhydrase genes was shown in Arabidopsis plants under drought, leading to an increase in the hydrogen sulfide generation [81]. An increase in the number of L-cysteine desulfhydrase transcripts and H2S content in alfalfa and cucumber was also revealed under the stressful concentrations of NaCl [82, 83].
A change in the hydrogen sulfide content in response to toxic doses of heavy metals and aluminum has been studied at a number of objects. In Arabidopsis, it increased under the influence of Cr6+ [84]. A similar effect was found in zucchini when exposed to nickel salts [85]. The activity of L-/D-cysteine desulfhydrases and β-cyanoalanine synthase in soybean plants increased under the influence of aluminum salt, and, consequently, the endogenous content of hydrogen sulfide also raised up [86].
2.3. Carbon Monoxide
CO in animals is considered the second most important GT after NO [87]. The carbon monoxide functions in animals as a neurotransmitter and inhibitor of platelet aggregation were investigated in the 1980-90s [10]. The effect of gaseous CO on physiological processes in plants was revealed later, although, CO as a gasotransmitter of plant cells is still much less studied than NO and H2S. To date, experimental data has been obtained indicating the involvement of CO in the regulation of plant growth and development [88, 89], in particular, seed germination [90], root development [91, 92], slowing down the aging of leaves and fruits [93, 94], as well as in the control of stomatal movements [95, 96].
Heme oxygenase is considered to be the main enzymatic source of carbon monoxide in plants. This enzyme catalyzes the stereospecific cleavage of heme to biliverdin-IXα with the release of Fe2+ and carbon monoxide [97] (Fig. 1C). To date, genes encoding heme oxygenase have been found in a wide range of organisms, including higher plants, red algae, cryptophytes, and cyanobacteria [97-100]. Plant heme oxygenases make up a small family of four genes. One subfamily unites HO1-like genes (including HO3 and HO4 of Arabidopsis thaliana), the other – HO2 genes [101, 102]. HO2 protein is the only member of the HO2 subfamily and is not a true heme oxygenase [102]. All the four genes of the family in A. thaliana are transcriptionally active, with significantly overlapping expression patterns [102]. It has been shown that HO1 is the most intensely expressed gene in plants [103].
In plant cells, heme oxygenase-1 was found in mitochondria [97] and chloroplasts (mainly in their stroma) [98]. Presumably, heme oxygenase is not the only source of carbon monoxide in plant cells. It was shown that in the soybean’s leaves and roots, the enhancement of CO generation under the salt stress did not correlate with the activity of heme oxygenase [103]. It is assumed that CO can be formed as a result of the destruction of heme-methylene bonds in a non-enzymatic way. Generation of carbon monoxide is also possible during lipid peroxidation and the metabolism of ureides (for example, purine) [103]. The pathways for CO elimination from plant cells have not been sufficiently explored yet. One of the main ways considered to inactivate CO is its binding to hemoglobin [104].
To date, research data has been obtained on the role of CO in the development of plant’s adaptive responses to the different abiotic stresses, its cross-links with other signaling molecules and plant hormones during the formation of defense reactions [10]. For instance, studies conducted on a number of objects have shown an increase in the carbon monoxide synthesis under osmotic stresses caused by PEG or high salinity [105-108]. It was found that germination of seeds of Burmese grape (Baccaurea ramiflora) under cold conditions prompted a transient increase in the activity of heme oxygenase-1 as well as in the CO generation [109]. Hyperthermia also affected tobacco plants causing heme oxygenase-1-dependent synthesis of CO, which, in turn, induced an increase in the jasmonic acid formation and associated protective reactions [110].
3. POST-TRANSLATION PROTEIN MODIFICATION AS A KEY MECHANISM OF GASOTRANSMITTER’S BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS
The actions of NO and H2S at the molecular level are associated with the regulation of the state and functional activity of proteins through post-translational modifications (PTM), which include S-nitrosation, tyrosine nitration, metal nitrosylation, and persulfidation [19, 33, 69, 111,]. The effect of these PTMs on a target protein can be positive, negative, or neutral. In any way, NO and H2S can compete with each other for the targets – specific Cys residues. Also, the GT interaction with functional groups of proteins depends upon the redox environment in the cell, which may differ depending on the development of plants and stress conditions [33].
3.1. PTM Involving NO
It is currently believed that NO is ideal for the role of a signaling molecule that realizes its potential in redox modifications of proteins [43]. One of the most important mechanisms of NO-modification of proteins for the regulation of cellular processes is S-nitrosation (Fig. 2A) – a covalent coupling of the NO group to -SH residues of cysteine with the formation of S-nitrosothiol (SNO) [33]. S-nitrosation is a reversible process that is considered to be a cellular switch that regulates the function of target proteins. It is believed that many cellular processes in plants, including those related to the response to environmental factors and immune function, depend on the S-nitrosation of proteins. S-nitrosation of proteins occurs without the involvement of enzymes [112]. However, this process is very specific, since it depends not only on the proximity between NO and the target protein but also on the amino acid sequence and conformation of the protein [113]. Also, S-nitrosation depends on the reactivity of the nitrosating agent (for example, NO+ or N2O3) and the redox potential of the microenvironment [112, 114].
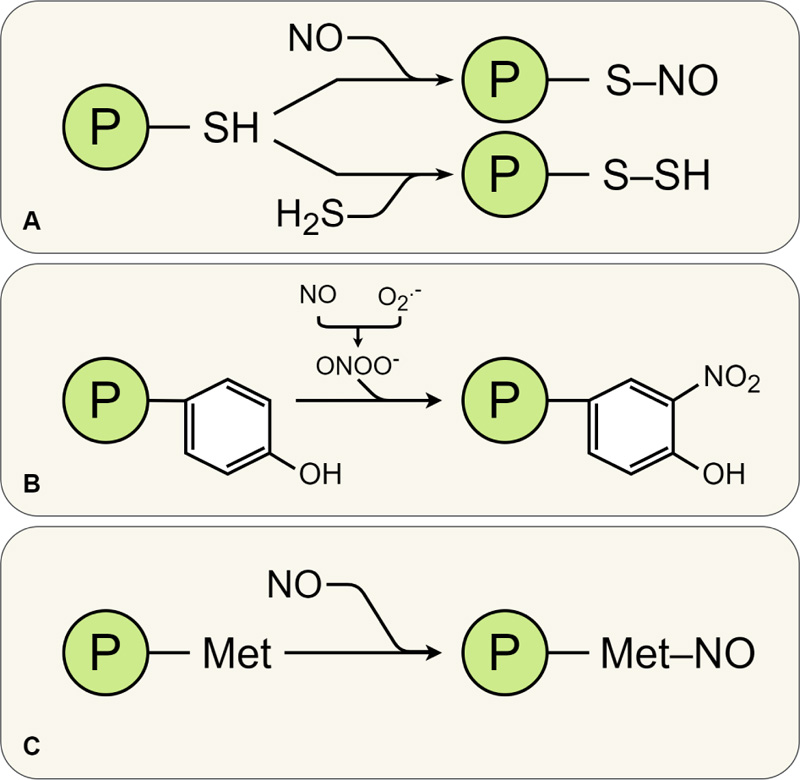
S-nitrosation of glutathione, leading to the formation of nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), is also of regulatory importance [115]. In particular, this compound causes redox modification of a number of regulatory proteins, for example, ethylene-sensitive transcription factors. Reactions of protein denitrosation are carried out with the participation of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase and thioredoxin [116]. Thus, in general, the degree of S-nitrosation of proteins depends on many factors, including the activity of the S-nitrosoglutathione reductase/thioredoxin/thioredoxin reductase system. To date, hundreds of proteins have been established which are regulated by S-nitrosation [117, 118].
| Protein | Plant Species | Modification Type | Activity Change | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase | Nicotiana tabacum | Heme nitrosylation | Inhibition | [122] |
| Catalase | Antiaris toxicaria | S-nitrosation | Activation | [109] |
| Cu/Zn-SOD | Arabidopsis thaliana | Tyrosine nitration (Tyr63) | Inhibition | [123] |
| Mn-SOD | Arabidopsis thaliana | Tyrosine nitration (Tyr63) | Inhibition | [124] |
| Fe-SOD | Arabidopsis thaliana | Tyrosine nitration (Tyr63) | Inhibition | [124] |
| Fe-SOD |
Brassica juncea |
S-nitrosation | Activation | [125] |
| Fe-SOD | Trypanosoma cruzi | Tyrosine nitration (Tyr35) | Inhibition | [126] |
| Ascorbate peroxidase | Nicotiana tabacum | Heme nitrosylation | Inhibition | [122] |
| Ascorbate peroxidase | Arabidopsis thaliana | S-nitrosation (Cys32) | Activation | [127] |
| Ascorbate peroxidase | Pisum sativum | S-nitrosation (Cys32) | Activation | [128] |
| Ascorbate peroxidase | Pisum sativum | Tyrosine nitration (Tyr5 and Tyr23) | Inhibition | [128] |
| Monodehydroascorbate reductase | Pisum sativum | S-nitrosation | Inhibition | [129] |
| Monodehydroascorbate reductase | Pisum sativum | Tyrosine nitration | Inhibition | [129] |
| S-nitrosoglutathione reductase | Solanum lycopersicum | S-nitrosation | Inhibition | [130] |
| NADPH oxidase | Medicago truncatula-Sinorhizobium | S-nitrosation | Inhibition | [131] |
| α-tubulin | Nicotiana tabacum | Tyrosine nitration (Tyr450) |
Activation (increase microtubule dynamics) | [19, 111] |
Another mechanism of post-translational modification of proteins under the NO influence is the reaction of nitration of tyrosine residues. This process is carried out mainly by peroxynitrite (ONOO–) and nitrogen dioxide radical (•NO2) [116]. Peroxynitrite is formed as a result of the NO reacting with a superoxide radical. Peroxynitrite then modifies the protein by adding a nitro group to the phenolic ring at position 3 (Fig. 2, A). Within a protein, not all tyrosine residues are sensitive to nitration. This process depends on the conformational state of the protein and the redox environment [116]. Also, the intensity of nitration, presumably, depends on the concentration of peroxynitrite, which can decrease due to its interaction with GSH, porphyrins, and carbonyl compounds [119].
Tyrosine nitration of proteins is one of the markers of nitrosative stress [120]. It is believed that protein nitration is an irreversible process; however, denitrase enzymes have been found in animals [116], which makes it likely that a similar process might also exist in plants. As for plants, we were the first to discover the nitrotyrosylation of α-tubulin, the main protein of microtubules. We have also determined the localization of nitrotyrosine on different types of mitotic microtubules, in particular those involved in the construction of the preprophase ribbon, mitotic spindle, and phragmoplast. It was found that such nitrotyrosylation does not lead to significant changes in the structural organization of microtubules in plant cells. However, it may be associated with the regulation of their dynamic properties and interaction with kinesin [111]. Although this post-translational modification is considered by some authors as a marker of nitrosative stress [120], we have shown that it can also be involved in the regulation of the functions of microtubule proteins that are directly involved in plant cells growth and division.
Another NO modification of proteins – nitrosylation of metal-containing proteins – occurs during the NO interaction with transition metal ions that make up metalloproteins, and leads to the formation of metal-nitrosyl complexes (Fig. 2). NO can bind to various metal-containing centers (Fe, Cu, Zn) of metalloproteins [114, 121]. Formation of metal-nitrosyl complexes causes reversible conformational changes in proteins and changes their structure and/or functional activity [112]. Currently, the list of enzymatic proteins for which the effects of positive (activation) or negative (inhibition) NO-modification have been established is constantly expanding (Table 1).
It should be noted that the post-translational modification of proteins depends not only on the possibility to contact NO and other reactive nitrogen species but also on the presence of other molecules capable of interacting with functional groups of proteins, in particular, hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen sulfide [118]. The issues of gasotransmitter’s competing for targets are discussed below.
3.2. PTM with Involvement of H2S
The primary molecular effects of H2S are believed to be related to persulfidation – conversion of the cysteine thiol group (-SH) into the corresponding persulfide (-SSH) [132]. This PTM is reversible [33, 133]. The interaction of hydrogen sulfide with protein disulfides is also possible, in which the reduced and persulfided residues are formed [134]:
R–SS–R + H2S → R–SSH + R–SH
Persulfide adducts demonstrate an increased nucleophilicity compared to the thiol group and, therefore could be more reactive [133]. Persulfidation is assumed to be widespread and to modify even more proteins than ROS and NO do, although the latter are studied better [135]. The mechanism of modification of specific targets by hydrogen sulfide is still not fully understood, since the direct reaction of H2S and thiol groups is thermodynamically unfavorable [132].
Currently, persulfide groups are considered important components of cellular signaling. Cysteine persulfide (CysSSH) and glutathione persulfide (GSSH) are recognized as key redox regulators [133]. The most common proteins with their state-regulated by persulfidation, are peroxiredoxins [134], which are also among the key cellular redox regulators [136]. At the same time, data obtained by methods of bioinformatics indicate that up to 5% of the plant cell proteome can undergo persulfidation [137]. Persulfidated proteins may include enzymes of glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle, Calvin cycle, and starch biosynthesis. Persulfidation is considered a simple and effective way to protect proteins from oxidative damage. In compartments with active ROS production, for example, in chloroplasts, there is a large amount of persulfidated proteins [138]. Persulfides act as good ROS scavengers.
Gotor et al. [139] suggested a model of interactions between ROS, H2S, and proteins, which provides the protection for the latter. According to this model, ROS, formed as a result of the light reaction of photosynthesis or due to stress processes, can lead to the oxidation of sulfides to H2S2 or polysulfide (H2Sn), which can react with thiol residues in proteins to form persulfides (-SSH). Thiolate (-SH) residues in proteins can be oxidized by ROS to form disulfide bridges (-SS-) or (under constant oxidizing conditions) sulfenic (-SOH), sulfinic (-SO2H), and sulfonic acid residues (-SO3H). Free H2S can react with sulfenic acid residues to form persulfidated proteins (-SSH). Persulfidated proteins, exposed to light, can be reduced by the ferredoxin/thioredoxin reductase/thioredoxin system. But in the dark or in non-photosynthetic tissues, the reduction of persulfided proteins can be provided by the NADPH thioredoxin reductase/thioredoxin system [139]. Persulfidation is one of the mechanisms regulating the activity of a number of antioxidant enzymes. For example, the Cys32 oxidation in the ascorbate peroxidase (APX1) molecule leads to its inactivation, and the Cys32 persulfidation with H2S, as well S-nitrosation with NO, stimulates the enzyme activity [118]. At the same time, persulfidation was shown to severely inhibit catalase [140]. Along with the enzymes of the antioxidant system, hundreds of proteins can be targets for both S-nitrosylation and persulfidation. For example, it was shown for Arabidopsis that 639 proteins are targets for these two processes, and 85% of them undergo persulfidation or S-nitrosation [141]. It has been shown on other objects that targets for S-nitrosation and persulfidation overlap by 36% [142]. One way or another, S-nitrosation and persulfidation compete with each other, as well as with other post-translational modification processes (S-glutathionylation, S-cyanylation, S-acylation, and S-sulfenylation) [33]. The predominant course of this or that process depends on the subcellular redox environment, which, in turn, depends on the constitutive and externally induced cellular physiological and biochemical processes [33].
Persulfidation is probably one of the components of the toolkit for gene expression regulation. The transcriptomic investigation carried out on Arabidopsis plants showed that treatment with exogenous H2S caused significant changes in the expression of numerous genes. H2S treatment, in particular, enhances the expression of genes encoding transcription factors and chromatin modifiers [141, 143]. The study of the tomato plant’s genes expression during the roots treatment with NaHS showed that 5349 genes were activated, and 5536 genes were suppressed [144]. A number of studies have shown the role of sulfide in the modification of histones and changes in the chromatin structure, which is a component of epigenetic regulation [118].
Nevertheless, in general, the data which would allow to link the persulfidation of certain protein targets with signaling processes that change the expression of specific genes is still incomplete. An interesting example is the hydrogen sulfide-dependent cold-induced synthesis of the secondary metabolite cucurbitacin in cucumber plants [79]. This terpenoid enhances plant resistance to pathogens, in particular to Phytophthora melonis. It was shown that its synthesis is associated with the persulfidation of two transcription factors that bind to the promoter of the cucurbitacin synthase gene. This process, which occurs in the cells of cucumber leaves, may be a consequence of the cold-induced (+4°C) increase of genes expression of various molecular forms of L-and D-desulfhydrases, and an increase in the hydrogen sulfide content [79].
Another example of a detailed study of the role of protein persulfidation in specific adaptive reactions of plants, can be the establishment of the role of hydrogen sulfide in stomatal reactions caused by ABA. Recent studies have shown that these effects are associated with the persulfidation of specific targets [145]. For example, H2S produced by L-desulfhydrase (DES1) positively regulates ABA signaling by persulfiding the protein kinase SnRK2.6 in guard cells. Persulfidation of Cys131 and Cys137 in the SnRK2.6 molecule facilitates the phosphorylating activity of the enzyme and its interaction with the factor ABA2 binding the response and additionally activates the expression of downstream genes. On the other hand, S-nitrosylation of Cys137 in the protein kinase SnRK2.6 inhibits its activity and negatively regulates ABA signaling in guard cells. It is assumed, that NO forms a feedback loop to fine tune the guard cells. At the same time, other enzymes, involved in the ABA-induced signal, undergo persulfidation, leading to an increase in activity: DES1 itself (this leads to self-amplification of the H2S signal), as well as the catalytic subunit of NADPH oxidase (RBOHD), which enhances ROS generation. It is assumed that protein modifications mediated by H2S, ROS, and NO regulate the redox homeostasis of the guard cells and ABA signaling [145].
3.3. PTM with CO Participation
The mechanisms regulating biological activity of CO differ significantly from those for nitrogen oxide and hydrogen sulfide. They are believed to be largely associated with the formation of coordination bonds with metals in the active centers of proteins, primarily the heme-containing ones [146]. On the whole, the question of the direct CO targets in plant cells still remains open. It is known that carbon monoxide can bind to the iron atom of the heme fragment of soluble guanylate cyclase, thereby activating the enzyme and increasing the production of the secondary intracellular messenger cGMP [9]. Over the recent years, the guanylate cyclase activity and cGMP in cells have been found in a number of plant species. At the same time, however, the existence of this enzyme in plants has not yet received molecular genetic confirmation, and the mechanisms of the relationship between carbon monoxide and cGMP remain unclear [147].
It should be noted that under the influence of exogenous carbon monoxide, the NO content in plant objects increased. The results obtained on various plant objects using inhibitory analysis indicate the participation of NO as a mediator in the implementation of the physiological effects of carbon monoxide. Such NO-dependent physiological processes are the induction of stomata closure by carbon monoxide and an increase in the salt tolerance of plants [95, 106, 148, 149]. Thus, NO in signaling pathways can be located below carbon monoxide. In this regard, it is possible that NO, rather than CO, binds to guanylate cyclase as a potential participant in the signaling chain. The literature discusses the issue of competition between CO and NO for binding to the active site of guanylate cyclase [9]. On the other hand, it should be noted that the functional interaction between NO and CO is apparently very complex and may be associated not only with a hypothetical protein with guanylate cyclase activity. There is evidence that it is possible to enhance the expression of the hemoxygenase gene and CO synthesis in plants under the influence of exogenous NO [88]. Thus, presumably, there are two-way connections between NO and CO in signaling networks, as well as competition for common targets, including many heme-containing proteins [11], among which there may be a protein with guanylate cyclase activity. Another example of such GT competition for targets can be the impact of carbon monoxide on the process of direct inhibition of heme-containing plant catalase and ascorbate peroxidase by nitric oxide [9].
4. INTERACTION OF GASOTRANSMITTERS BETWEEN THEMSELVES AT THE LEVEL OF SYNTHESIS
A number of works report that the action of nitric oxide can be mediated by hydrogen sulfide and vice versa. Thus, under the influence of SNP as a NO donor, an increase in the heat resistance of maize seedlings was observed as well as an increase in the content of endogenous H2S [63]. On the other hand, the H2S donor GYY4137 (morpholin-4-ium-4-methoxyphenyl [morpholino] phosphinodithioate) enhanced the positive affect of SNP on the heat resistance of seedlings. The authors conclude that hydrogen sulfide, as a signaling mediator, is located after nitric oxide [150].
However, another effect is also possible: hydrogen sulfide is able to induce NO synthesis in plants. The experiments on alfalfa plants have revealed an elimination of the positive effect of the hydrogen sulfide donor NaHS on salt tolerance and expression of antioxidant enzyme genes by the nitric oxide scavenger PTIO (2-phenyl-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide) [151]. The increase in heat resistance of wheat seedlings under the influence of NaHS was accompanied by a transient increase in the content of nitrate reductase-dependent nitric oxide [152]. The stomatal closure affect caused by hydrogen sulfide might also be mediated by nitric oxide, synthetized with the involvement of nitrate reductase. Thus, the treatment of the leave’s epidermis of Arabidopsis mutants, defective in the activity of two forms of nitrate reductase (nia1/nia2), with a hydrogen sulfide donor did not cause stomata closure [153]. At the same time, treatment with a nitric oxide donor caused the closure of stomata in nia1/nia2 plants; and exogenous NO also induced a similar effect in des1-1 and des1-2 plants, defective in hydrogen sulfide synthesis [153].
Nitric oxide can mediate some physiological effects of carbon monoxide. Thus, an increase in the salt tolerance of wheat plants by the CO donor, associated with the stabilization of ionic homeostasis and activation of the antioxidant system, was accompanied by an increase in the NO content and was eliminated by its antagonists [154]. The enhancement of lateral root formation by carbon monoxide in rapeseed also depended on the NO synthesis [95]. Treatment of wheat seedlings with the CO donor hemin, which increased their heat resistance, was accompanied by a nitrate reductase-dependent transient increase in NO synthesis. The NO scavenger PTIO and the nitrate reductase inhibitor sodium tungstate eliminated the stress-protective effect of the CO donor [155]. However, it should be noted that at the molecular level, the mechanisms of GT influence on the synthesis of each other remain largely unclear. It is quite possible that other mediators are involved in these processes, in particular, ROS and calcium ions.
5. CONNECTION OF GASOTRANSMITTERS WITH CALCIUM AS A KEY SIGNAL MEDIATOR
It is well known, that calcium is recognized as a universal mediator in cellular reactions of plant and animal organisms [156]. It is cytosolic calcium that can serve as a link for many signaling pathways, providing the formation of a signaling network of a plant cell [157]. The transmission of stress signals with the calcium participation occurs due to its ability to differentially interact with cellular proteins. It is also worth noting that an extremely important highly conservative calcium receptor is calmodulin [158, 159]. It regulates a number of proteins including some transcription regulating factors, ion channel proteins, enzymes of normal metabolic cycles, cytoskeletal proteins, chaperones, proteins involved in the transmission of hormonal signals [156, 159, 160].
5.1. Calcium and Nitric Oxide
A significant amount of experimental data indicates that calcium can participate both in the enhancement of nitric oxide synthesis in plant cells and in the transmission of its signals. Functional links between nitric oxide and calcium homeostasis are manifested when the plants are exposed to extreme factors. Thus, when the culture of seaweed Ulva compressa was exposed to copper ions, the content of nitric oxide and calcium ions in the cells increased [161]. At the same time, the treatment of cells with the NO scavenger eliminated an increase of the intracellular calcium concentration, and calcium antagonists nullified the effect of NO accumulation. The treatment of wheat seedlings with calcium antagonists (extracellular calcium chelator EGTA, nonspecific calcium channel blocker lanthanum chloride, and phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C inhibitor neomycin) eliminated the increase in nitric oxide content in roots caused by short-term hardening and prevented the development of heat resistance [162].
It is well known that NO synthase in animals is activated under the influence of calcium/calmodulin [34, 163]. However, as already noted, the recent molecular genetic studies have indicated the absence of typical animal NO synthase in higher plants. Nevertheless, it is assumed that cellular peroxisomes in higher plants contain proteins, other than NO synthase, but capable of generating NO using L-arginine as a substrate. This reaction, like the one catalyzed by animal NO synthase, requires the presence of calmodulin and calcium ions [43]. The reductive pathway of nitric oxide synthesis in plants, associated primarily with the activity of nitrate reductase, also appears to be calcium-dependent. The effect of plant nitrate reductase activation by calcium ions and its inhibition in the presence of a calcium chelator has been shown in vitro quite some time ago [164]. Activation of this enzyme was also found in intact plants under the influence of exogenous calcium [165]. The stress-protective effect of calcium may be associated with the synthesis under its influence of the NO and other signaling molecules. Thus, the positive effect of calcium chloride on the heat resistance of wheat seedlings was accompanied by an increase in the content of endogenous NO and was eliminated by the action of the NO PTIO scavenger [166]. Exogenous Ca added to Vigna radiata seedlings, exposed to Cd stress, decreased the Cd accumulation and increased the activity of nitrate reductase and L/D-cysteine desulfhydrase, which led to an increase in the synthesis of NO and H2S [167]. NO antagonists, similarly to calcium antagonists, eliminated the protective effect of exogenous calcium and a nitric oxide donor. The authors believed that Ca acted both above and below the NO signals.
Treatment with exogenous calcium mitigated the manifestation of oxidative stress, the loss of chlorophyll pool, and the growth inhibition of mustard seedlings caused by the arsenic action [168]. Thus, the nitric oxide content in the leaves increased under the calcium influence. Treatment with the NO antagonists PTIO and L-NAME eliminated the stress-protective effects of calcium. The authors concluded that NO plays a critical role in Ca2+-mediated signaling [168].
On the other hand, it is known that nitric oxide donors contribute to an increase in the content of cytosolic calcium in plant cells [169]. In animal cells, NO-induced opening of calcium channels is mediated by cGMP. It is formed by the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide, which is considered one of the NO receptors [170]. However, as previously noted, homologues of soluble guanylate cyclase in higher plants have not yet been identified using molecular genetic methods [147], though, a homologue of this protein was found in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [171]. In general, there are numerous experimental data which indirectly indicate the existence of NO-mediated formation of cGMP in plant cells. For instance, it was shown that levels of both NO and cGMP increased in Arabidopsis plants under cold stress. Nitrate reductase inhibitor, sodium azide, neutralized the cold-induced increase in tissue cGMP [172]. Moreover, the cGMP accumulation was eliminated by treating plants with the guanylate cyclase inhibitor 6-anilinoquinoline-5,8-quinone. Another work showed that this inhibitor purged an increase in the cGMP content in Arabidopsis seedlings caused by the action of the NO donor SNP [173]. Transgenic plants Nicotiana plumbaginifolia express calcium-sensitive protein apoaequorin. Influenced by SNP, a nitric oxide donor, there was a transient raise in the level of intracellular calcium, which was suppressed by the guanylate cyclase inhibitor 6-anilinoquinoline-5,8-quinone [172].
Another mechanism of the NO, affecting the state of calcium channels, can be the modulation of proteins phosphorylation, including protein kinases and protein phosphatases [30]. It is well known that in animals, NO modulates the activity of various classes of protein kinases, but in plants, NO-induced modulation of protein kinases requires further research and clarification. It has been shown that NO donors induce the protein kinases activity in Arabidopsis leaves [174] and cucumber explants [175]. However, these affects have not been confirmed by molecular genetic methods. The cytosolic calcium concentration is induced by nitric oxide and depends on the activity of protein kinases. This dependence was demonstrated on bean cells and suspension culture of tobacco cells using the corresponding inhibitors – K252a and staurosporine. The latter eliminated the increase in [Ca2+]cyt caused by the NO donors [176, 177].
5.2. Calcium and Hydrogen Sulfide
A functional interaction between calcium and hydrogen sulfide is an important component of stress signaling in plants [67, 178]. Calcium is involved both in the regulation of hydrogen sulfide synthesis and in the transduction of its signals. The use of exogenous calcium and calmodulin stimulated L-cysteine desulfhydrase in cultured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cells, which led to an increase in the concentration of endogenous H2S [179]. The formation of hydrogen sulfide in Arabidopsis seedlings, caused by the action of chromium (Cr6+), turned also to depend on calcium and calmodulin [180]. The treatment of plants with EGTA removed the chromium-induced increase in the expression of the L-cysteine desulfhydrase gene and the increase in the content of H2S [84]. Conducted on the same object, the study also showed that calcium, combined with calmodulin-2, interacts with the transcription factor TGA3, which is necessary for its binding to the promoter of the L-cysteine desulfhydrase gene and enhancing its expression. The increase in the hydrogen sulfide content in cells of roots and leaves of zucchini, caused by the toxic effect of nickel, was eliminated by the extracellular calcium chelator EGTA, the blocker of voltage-gated calcium channels verapamil, and the calmodulin antagonist trifluoperazine [85].
Calcium is also involved in H2S signaling. The increase in heat resistance of the suspension culture of tobacco cells by the action of the H2S donor NaHS was nullified under the influence of the calcium chelator EGTA, the calcium channel blocker La3+, as well as the calmodulin antagonists chlorpromazine and trifluoperazine [67]. At the same time, the stress-protective effect of the H2S donor was enhanced by the simultaneous use of the calcium ionophore A23187 or exogenous Ca2+. These results are consistent with the data on the inhibition of the hydrogen sulfide effect on the heat resistance of wheat coleoptile cells, the ROS generation, and the activity of antioxidant enzymes upon treatment with EGTA and neomycin, an inhibitor of phospholipase C, which is involved in regulation of calcium homeostasis [181].
The protective effect of sodium hydrosulfide on mogar plants, exposed to the toxic influence of Cr6+, was enhanced when they were treated with exogenous calcium (Fang et al. 2014). At the same time, the effect of the extracellular calcium chelator, EGTA, on the contrary, nullified the manifestation of the hydrogen sulfide physiological effect. Calcium is involved in the stomata closure caused by hydrogen sulfide. It was found that H2S regulates stomatal movement through interaction with Ca2+ and ROS [179]. NaHS treatment induced the A. thaliana stomata closure, and these effects were attenuated by EGTA (Ca2+ chelator) and nifedipine (the blocker of plasma membrane calcium channel). In addition, H2S activated the expression of the NADPH oxidase and cell wall peroxidase genes, which, in turn, caused the accumulation of H2O2 in guard cells. At the same time, EGTA treatment eliminated these effects of hydrogen sulfide [179]. It has also been established that a number of proteins that regulate the stomatal activity, such as calcium-dependent protein kinases CPK3 and CPK6 [182, 183] and MAP kinases (MPK3, MPK4, and MPK6) [184, 185], are targets for persulfidation and sulfenylation [141, 186].
5.3. Calcium and Carbon Monoxide
The CO effect on calcium homeostasis in plants requires further research. It has been known for a long time that carbon monoxide binds to an iron atom of the heme fragment in soluble guanylate cyclase, thereby activating the enzyme and increasing the production of the secondary intracellular messenger cGMP [9]. This signaling pathway, causing an increase in the formation of cyclic nucleotides, can lead to the opening of calcium channels regulated by them. However, due to the lack of molecular genetic evidence for the presence of guanylate cyclase in higher plants, it can only be considered as hypothetical. For animal cells, there is also data on the possibility of CO to influence the ion channels proteins, including L-type calcium channels [187]. However, it is assumed that these effects may be mediated by the action of ROS produced in cells under the influence of CO. Some works, performed on plant objects, have shown the elimination of the physiological effect of carbon monoxide and its donors in the presence of calcium antagonists. Thus, the effect of hematin on the growth of wheat seedlings was eliminated by calcium antagonists EGTA and ruthenium red [188]. Our studies have shown that treatment of seedlings with 5 μM hemin, enhancing their heat resistance, caused a transient increase in the extracellular peroxidase activity and a raise in the ROS generation, followed by a boost in the activity of the antioxidant enzymes (SOD, catalase, and intracellular peroxidase) [189]. Neomycin, the chelator of extracellular calcium EGTA and the inhibitor of the inositol-1,4,5-phosphate formation, which reduces the calcium flow into cytosol from intracellular compartments, significantly eliminated these effects. Also, in the presence of EGTA and neomycin, there was no positive effect of hemin treatment on the state of membranes and the survival of seedlings after the damaging heating. It can be assumed that both extracellular and the deposited in intracellular compartments calcium is involved in the development of heat resistance of wheat seedlings exposed to the exogenous CO. The stress-protective action of CO also, presumably, involves ROS, which functionally interacts with calcium ions [189].
6. INFLUENCE OF EXOGENOUS GASOTRANSMITTERS ON RESISTANCE OF PLANTS TO ACTION OF ABIOTIC STRESSES
6.1. Low Temperatures
The positive effect of exogenous nitric oxide on resistance to low temperatures was established for plants of different species (Table 2). Thus, the treatment of Bermuda grass plants with SNP reduced the effects of the cold-induced release of electrolytes from tissues and an increase in the content of the lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde in cells. The plants, exposed to low temperatures and treated with the NO donor, showed an increased activity of antioxidant enzymes [190]. The SNP effect on Arabidopsis plants promoted an increase in the proline content, while the NO scavenger cPTIO, as well as okadaic acid, an inhibitor of one of the enzymes of NO synthesis (nitrate reductase), prevented the proline accumulation during cold acclimation (Table 2).
| Donor or Scavenger of Gasotransmitter, Concentration | Plant Species | Physiological Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Temperatures | |||
| NO donor SNP (100 µM) | Cynodon dactylon | Protection of biomembranes from oxidative damage and an increase in the activity of SOD, peroxidase and catalase, increased content of chlorophyll and the intensity of photosynthesis | [190] |
| NO scavenger cPTIO (400 µM), NR inhibitor okadaic acid (1 µM) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Decreased plant survival after freezing at –7°C (4h), decreased proline content during cold hardening, inhibition of proline accumulation caused by cold acclimation | [191] |
| NO donor SNP (50 or 200 µM) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Increased proline content, increased plant survival after freezing at –7°C (4 h) | [191] |
| NO donor SNP (100 µM) | Juglans regia | Decrease in lipid peroxidation intensity under low temperatures, increased content of GSH, sugars, proline, and phenolic compounds | [192] |
| NO donor SNP (200 µM) | Triticum aestivum, Secae cereale | Increased ability to cold hardening, increasing the content of proline, sugars, flavonoid compounds, activity of SOD and peroxidase | [193] |
| NO donor SNP (200 µM) | Cucumis sativus | Increased content of transcripts and activity of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, increased content of sugars, starch, ascorbic acid, and GSH | [194] |
| NO donor SNP (100 µM), NO scavenger cPTIO (100 µM) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Preservation of structure of actin filaments under the SNP influence and enhancement of their disorganization in the cPTIO presence under hypothermic conditions | [195] |
| H2S donor NaHS (500 µM) | Cynodon dactylon | Increased activity of catalase, guaiacol peroxidase, and glutathione reductase under hypothermia | [196] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100 or 500 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Increased survival at negative temperatures, increased activity of guaiacol peroxidase and catalase, sugar and proline content, increased PAL activity and flavonoid content | [197, 198] |
| CO water solution (50%), hematin (10 µM) | Baccaurea ramiflora | Increased seed germination, decreased H2O2 content, increased expression of glutathione reductase and ascorbate peroxidase genes, increased activity of ascorbate peroxidase, monodehydroascorbate reductase, increased GSH content | [109] |
| High Temperatures | |||
| NO donor SNP (250 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Mitigation of the oxidative stress manifestation, preservation of the chlorophyll pool under stress conditions, an increase in the activity of enzymes of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle under conditions of hyperthermia, an increase in the content of ascorbate and GSH | [199] |
| NO donor SNP (200-500 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced survival after heating at a potentially lethal temperature. Increased activity of SOD, catalase, and guaiacol peroxidase under high temperature conditions |
[200, 201] |
| NO donor SNP (150 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced expression of HSP17 and HSP26 genes as well as SOD, catalase, and guaiacol peroxidase | [202] |
| Arginine (5 mM) | Triticum aestivum | Increased survival of seedlings after heating at a potentially lethal temperature, increased activity of catalase and guaiacol peroxidase | [203] |
| Sodium nitrate (20 mM) | Triticum aestivum | Increased survival of seedlings after heating at a potentially lethal temperature, increased SOD and catalase activity | [203] |
| NO donor SNP (100 µM), NO scavenger cPTIO (100 µM) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Preservation of the integrity of microtubules under the SNP action under conditions of hyperthermia, and enhancement of their depolymerization in the presence of cPTIO | [28] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100 µM) | Nicotiana tabacum | Reduced oxidative damage | [67] |
| H2S donor GYY4137 (100 µM) | Zea mays | Reduced oxidative damage | [150] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Increased survival after heating at a potentially lethal temperature, increased activity of SOD, catalase, and guaiacol peroxidase | [181] |
| H2S donors NaHS (50 μM) or GYY4137 (10 μM) | Populus trichocarpa | Increase in the activity of enzymes of ascorbate-glutathione cycle under hyperthermia | [110] |
| H2S donor NaHS (200 µM) + NO donor SNP (100 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced plant growth under conditions of hyperthermia, mitigating oxidative damage, increasing the activity of SOD and catalase | [204] |
| CO donor hemin (5 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Increased survival after heating at a potentially lethal temperature, increased activity of SOD, catalase, and guaiacol peroxidase | [205] |
| Drought | |||
| NO donor SNP (200 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced seedling growth, maintaining a high relative water content under the action of 15% PEG 6000, reducing oxidative damage | [206] |
| NO donor SNP (500 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced plant growth, increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes under drought conditions | [207] |
| NO donor SNP (2 mM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced plant growth, increasing proline content under drought conditions | [207] |
| NO donor SNP (100 µM) | Zea mays | Increasing the relative water content, mitigating the oxidative stress manifestations, increasing the activity of catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, SOD, and glutathione-S-transferase | [208] |
| Inhibitor of H2S synthesis aminooxyacetic acid (300 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Increasing of drought-induced oxidative damage to plants | [209] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100 µM) | Cynodon dactylon | Increased activity of peroxidase, catalase, and glutathione reductase, stabilization of the pool of reduced glutathione under dehydration conditions | [196] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100; 500 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced plant growth during soil drought, increased superoxide dismutase activity, content of proline and anthocyanins | [210] |
| H2S donor NaHS (500; 1000 µM) | Carthamus tinctorius | Mitigation of oxidative damage, preservation of the chlorophyll pool and ion homeostasis during soil drought | [211] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100 µM) | Spinacia oleracea | Increased accumulation of proline, glycine betaine, and trehalose under osmotic stress | [212] |
| CO donor hematin (1 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced seed germination in PEG 6000 presence, protection against oxidative damage, increased amylase activity | [106] |
| High salinity | |||
| NO donor SNP (100 µM) | Brassica juncea | Increased activity of SOD, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, glutathione reductase, GSH content | [213] |
| NO donor SNP (10 µM) | Brassica napus | Enhanced expression of genes for ascorbate peroxidase, Cu/Zn-and Mn-SOD, mitigation of oxidative damage, and inhibition of root growth | [214] |
| NO donor S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (50 µM) | Cicer arietinum | Increased activity and increased expression of genes for antioxidant enzymes – SOD, catalase, and ascorbate peroxidase | [215] |
| NO donor SNP (50 µM) | Chenopodium quinoa | Enhanced seed germination during salinity, increased amylase activity | [216] |
| H2S donor NaHS (50 µM) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Reducing water deficit, reducing oxidative damage and membrane permeability, increasing the activity of SOD and catalase | [217] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100 µM) | Triticum aestivum | Enhanced seed germination in NaCl presence | [218] |
| H2S donor NaHS (100 µM) | Medicago sativa | Maintaining ion homeostasis | [151] |
| H2S donor NaHS (5-20 µM) | Cucumis sativus | Maintaining ion homeostasis | [219] |
| CO donor hematin (1 mM) or CO solution (5%) | Oryza sativa | Enhanced seed germination, increasing amylase activity, increasing the amount of sugars in seedlings, increasing SOD and catalase activity | [220] |
| CO solution (50%) | Truticum aestivum | Mitigation of root growth inhibition, prevention of programmed death of root cells, decrease in gene expression and activity of NADPH oxidase, increase in SOD activity, enhancement of Mn-SOD gene expression | [105] |
| CO donor hematin (1 µM) | Truticum aestivum | Enhanced expression of the Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase gene, decreased expression of the proline dehydrogenase gene, accumulation of proline | [221] |
| UV-B irradiation | |||
| NO donor SNP (10, 100 µM) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Amplification of plant cells resistance to the action of UV-B by involving myo-inositol in metabolism through inositol-3-phosphate synthase 1 (IPS1), a key enzyme for biosynthesis of myo-inositol | [222] |
| NO donor SNP (10, 100 μM) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Protection of microtubules from UV-B stress, enhancement of their polymerization, restoration of the original organization of microtubules, growth of shoots and roots | [223] |
| H2S donor NaHS (1,0 mM) | Hordeum vulgare | Prevention of oxidative damage, reduced release of electrolytes from tissues after stress exposure | [224] |
SNP treatment of walnut shoots in vitro increased their resistance to low temperatures above zero, contributing to accumulation of low-molecular-weight protectors [192] (Table 2). It is noteworthy that in this case, the exogenous effect of the NO donor stimulated the generation of endogenous nitric oxide. This effect was abolished by the action of inhibitor of animal NO synthase L-NAME, but not of nitrate reductase (sodium tungstate). The authors conclude about the oxidative pathway of NO formation under the action of its donor. The priming of wheat and rye seeds with SNP enhanced frost resistance during cold hardening (Table 2). At the same time, the treatment of unhardened seedlings with the NO donor had almost no effect on their frost resistance [193].
There are evidences of enhancing cold resistance of heat-loving plants under the influence of the NO donor SNP, in particular, of cucumber (Table 2). One of the mechanisms of the exogenous NO protective effect on plants under conditions of hypothermia may be stabilization of the cytoskeleton structure. It has been shown that treatment with the NO donor SNP promotes the preservation of the original organization of actin filaments in the epidermal cells of Arabidopsis primary roots exposed to the temperature of 0.5° [195]. The low temperature as such, as well as the NO scavenger (cPTIO), cause disorganization or destroying of the actin filament network (Table 2).
The influence of hydrogen sulfide donors on the plant adaptation to cold has not been properly explored yet. However, according to Shi, the activity of antioxidant enzymes in Cynodon dactylon plants increased upon treatment with NaHS before the plants were exposed to a hardening temperature of 4°C. The plants also survived subsequent freezing at –10°C [196]. Furthermore, pretreatment of hardened and unhardened wheat seedlings with 0.1 or 0.5 mM NaHS improved their survival rate after their subsequent freezing at –5°C (Table 2). One of the mechanisms of the H2S donor’s positive effect on the resistance of wheat seedlings to hypothermia is the accumulation of flavonoid compounds with high antioxidant activity and reducing the effects of secondary oxidative stress. These processes depend on the activity of phenylalanine ammonium lyase [197]. The effect of exogenous carbon monoxide on the processes of plant adaptation requires deeper and more thorough investigation. It was shown that treatment of germinating Burmese grape seeds under low-temperature conditions, with hematin or a CO solution enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes and the formation of low-molecular-weight antioxidants [109] (Table 2).
6.2. High Temperatures
The effects of strengthening the heat resistance of plant objects under the influence of NO donors have been reported by many researchers over a prolonged period of time [27, 225]. For example, treatment of 8-day-old wheat sprouts with 0.25 mM SNP increased their resistance to a subsequent heat stress [199] (Table 2). Similar results were obtained on intact roots and isolated coleoptiles of wheat. Treatment with 200-500 µM SNP promoted their survival after potentially lethal heating, as well as an increase in the activity of antioxidant enzymes (Table 2). Treatment of wheat plants with SNP under heat stress also promoted an increase in the expression of genes for individual HSP17 and HSP26 [202] (Table 2). Plant resistance to hyperthermia also increased under the influence of compounds that are natural substrates for the NO formation – L-arginine and nitrate [203]. Treatment of wheat seedlings with these compounds increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes.
One of the reasons for the positive effect of exogenous NO on plant heat resistance may be the involvement of this signaling molecule in the functioning of key elements of cytoskeleton. It was shown that the treatment of Arabidopsis roots with the donor of nitric oxide SNP promoted the preservation of the structural integrity of microtubules under the action of high temperature, while the treatment with the NO scavenger cPTIO caused the opposite effects [28] (Table 2).
An increase in the heat resistance of a number of plant objects also occurs under the influence of hydrogen sulfide donors. Treatment of a suspension culture of tobacco cells with NaHS mitigated heat-induced oxidative damage [67] (Table 2). The oxidative damage caused by hyperthermia in maize seedlings was also reduced under the action of morpholin-4-ium 4 methoxyphenyl (morpholino) phosphinodithionate (GYY4137), a slow-acting donor of hydrogen sulfide (Table 2).
An increase in the heat resistance of isolated wheat coleoptiles under the influence of the hydrogen sulfide donor led to an increase in the activity of key antioxidant enzymes. This effect was inhibited by calcium antagonists and depended on the ROS generation, which occurs with the participation of NADPH oxidase [181]. One of the mechanisms of the direct effect of hydrogen sulfide on redox balance under stress conditions can be activation of certain enzymes, for example, catalase and ascorbate peroxidase, by persulfidation [142, 226].
Cheng [110] showed that hydrogen sulfide donors mitigated oxidative damage to poplar plants caused by an excess of ROS and RNS under hyperthermia. Treatment with hydrogen sulfide donors increased the activity of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle enzymes (Table 2). A number of mechanisms of the stress-protective effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on plants during hyperthermia were analyzed in a review by Ali et al. [29]. It is about an increase in gene expression for catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, glutathione reductase, some forms of SOD, as well as HSP70, HSP90, HSP80, and aquaporins in the presence of hydrogen sulfide donors.
Recently, data were obtained on a stronger stress-protective effect of a mixture of the nitric oxide donor SNP and the hydrogen sulfide donor on wheat plants under the conditions of hyperthermia (Table 2). Probably, these effects can be explained by the involvement of NO and H2S into a single signaling network acting in adaptation to high temperatures [152, 204].
There is still very little data available on the effect of exogenous carbon monoxide on the heat resistance of plants. The survival of tobacco cells in a suspension culture improved when a CO donor hematin was added to the medium [227]. It is noteworthy, that the stress-protective effect of this gasotransmitter was mediated by hydrogen sulfide since this effect was inhibited by H2S scavengers and synthesis inhibitors. Hemin was found to enhance the heat resistance of intact wheat seedlings [205]. This effect was accompanied by a transient increase in the hydrogen peroxide generation, activation of antioxidant enzymes, and led to the preservation of the integrity of membranes after the damaging heating (Table 2). However, it should be noted that the induction of heme oxygenase resulted not only in an increase in CO synthesis, but also in the formation of biliverdin, which has pronounced antioxidant properties. In this regard, some authors suppose that protection of plants from oxidative stress with the CO donors may be not due to carbon monoxide itself, but due to an increase in the content of biliverdin and products of its conversion in cells [228]. However, the elimination of the stress-protective effects of heme oxygenase inducers by CO scavengers still indicates the primary importance of carbon monoxide formation, which acts as a facilitator of many plant defense reactions [205].
6.3. Drought
It was shown that the resistance of wheat seedlings to osmotic stress, caused by PEG, strengthened under the influence of 200 μM SNP (Table 2), while 2 mM SNP aggravated the damage [206].
It was found that preliminary spraying of wheat plants with 0.5 or 2 mM solutions of the nitric oxide donor SNP mitigated the growth-inhibiting effect of soil drought on wheat plants [207]. That being said, the nitric oxide donor at a lower concentration (0.5 mM) enhanced the activity of the antioxidant enzymes SOD, catalase, and guaiacol peroxidase, but decreased the proline content in the drought conditions. The same donor at a higher concentration (2 mM), on the contrary, caused an increase in the proline content in the absence of a noticeable effect on the activity of antioxidant enzymes. Thus, the NO donor at different concentrations can activate different components of the stress-protective systems. Spraying corn plants with 100 μM SNP also improved their water status, promoted the preservation of chlorophyll pool during drought, increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes, and reduced the MDA accumulation [208].
An increase in plant drought resistance is also achieved by enhancing NO synthesis due to transgenesis. The corresponding examples are considered in review [27]. Overexpression of rat neuronal NO synthase (nNOS) in rice plants increased NO accumulation, which led to an increase in drought tolerance in transgenic plants. The transgenic Arabidopsis plants, overexpressing rat nNOS gene, also were more tolerant to the drought and other abiotic stresses, than not transformed. These plants differed in the increased level of antioxidants and osmolytes under dehydration [27].
Hydrogen sulfide, like NO, can strengthen the resistance of plants to the lack of moisture. Treatment of etiolated wheat seedlings with an inhibitor of hydrogen sulfide synthesis, aminooxyacetic acid, aggravated the damage under osmotic stress and reduced stress-induced enhancement in the expression of ascorbate peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and monodehydroascorbate reductase genes [209]. At the same time, the activity of antioxidative enzymes in Bermuda grass plants increased when they were treated with the hydrogen sulfide donor NaHS before osmotic stress [296] (Table 2). Treatment of green wheat plants with the solution of sodium hydrosulfide before a soil drought facilitated the SOD activity and prevented a stress-induced decrease in catalase and guaiacol peroxidase activity in leaves [210] (Table 2). Also, under the influence of a hydrogen sulfide donor during soil drought, the content of proline and anthocyanins, low-molecular-weight protectors, increased in the leaves of wheat plants (Table 2). Treatment with NaHS also strengthened the resistance of safflower to drought, which was expressed in a decrease in oxidative damage, an increase in the content of secondary metabolites, and stabilization of ionic homeostasis [211] (Table 2). In Spinacia oleracea L. plants, under the influence of a hydrogen sulfide donor in drought conditions, the content of glycine, betaine, and trehalose, which have osmoprotective and antioxidant properties, increased [212].
In general, many studies have shown strengthening of the resistance potential of plants of various species to drought by the NaHS action at a concentration of 10-1000 μM [138]. These effects are due to PTMs of a number of proteins, including antioxidant enzymes, and an increase in the accumulation of low-molecular-weight protective compounds (antioxidants, osmolytes) by plants. Another important mechanism of the hydrogen sulfide influence on the drought resistance of plants may be its participation in regulation of stomata state. Thus, it was shown that exposure to 100 μM NaHS for 90 min caused a decrease of the stomatal aperture in Arabidopsis plants [229]. Treatment of the epidermis of sweet potato leaves with 100 μM NaHS caused an increase in the relative number of completely closed stomata [230]. At the same time, Lisjak et al. [231, 232] showed an increase in a stomatal aperture in Arabidopsis and pepper plants after 2.5-hour treatment of the epidermis with 100 and 200 μM NaHS in the light. It was shown that after the treatment of separated Arabidopsis leaves with the organic hydrogen sulfide donor GYY4137 at a concentration of 100 μM, the stomata closed after 90 min. After 120 min, on the contrary, the aperture opening was observed and followed with closing by 180 min [233].
Thus, the effects of hydrogen sulfide donors on the state of stomata can have complex dynamics over the time. The reduction of the stomatal aperture and of the relative number of open stomata in Arabidopsis, caused by the hydrogen sulfide donor, was almost completely eliminated by the pretreatment of the leaves with a calcium channel blocker lanthanum chloride, extracellular calcium chelator EGTA, phospholipase C inhibitor neomycin, and an antagonist of the cyclic adenosine-5'-diphosphate ribose formation nicotinamide [234]. Also, the stomatal effect of the H2S donor was partially eliminated by the calmodulin antagonist chlorpromazine. Nullification of the effect of the hydrogen sulfide donor on the state of the stomatal apparatus of Arabidopsis leaves was also noted as a result of pretreatment of leaves with 1-butanol, an inhibitor of phospholipase D-dependent phosphatidic acid formation. Thus, the results obtained indicate that the calcium influx into the cytosol from various compartments, as well as the formation of lipid signaling mediators, are necessary for the implementation of the hydrogen sulfide effect on the stomata state [234].
Some works were dedicated to the investigation of the CO donor’s effect on the resistance of plants to the action of osmotic stress agents (Table 2). For instance, an intensification of wheat seeds germination was established in the presence of 25% PEG-6000 during treatment with hematin [106]. The effect of hematin was not manifested in the presence of heme oxygenase inhibitor, Zn-protoporphyrin IX, which indicates the specificity of effects of the hematin as a substrate of this enzyme. Treatment of sprouts with hematin facilitated activity of amylase, and of the antioxidant enzymes.
A number of studies have shown the effects of stomatal closure in plants treated with inducers of CO formation, which may be beneficial in drought. Thus, the closure of stomata in beans was revealed as the effect of hematin [235]. It has also been established that carbon monoxide can mediate the stomatal effects of ABA [95]. It is assumed that the closure of stomata after the CO influence may be due to its direct binding to proteins involved in the regulation of ion channels. However, the NO scavenger PTIO and the NOS inhibitor L-NAME eliminated the hematin effect on the stomatal aperture, which indicates that the effect is mediated by nitric oxide [96].
6.4. High Salinity
The influence of nitric oxide on the processes of adaptation of plants to salinity was manifested in rather diverse effects. It happens due to the NO influence on the processes of ion transport, antioxidant system, and accumulation of osmolytes [236]. Thus, an increase in the work of Na+/H+ antiporters and proton pumps of tonoplast under the salt stress was established to be caused by the NO donors [236]. Additionally, treatment of mustard with SNP reduced the hydrogen peroxide and MDA formation under salt stress (Table 2). At the same time, in the case of treatment with the NO donor SNP, an increase in the functioning of the antioxidant system was noted (Jahen et al., 2020). SNP treatment of rapeseed plants under salt stress increased the amount of S-nitrosylated proteins, while both gene expression and the activity of ascorbate peroxidase and various SOD forms raised up [214]. Another NO donor, S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine, caused an increase in the salt tolerance of chickpea plants, which was associated with an increase in the activity and increased expression of genes of a number of antioxidant enzymes [215] (Table 2).
Pretreatment of Chenopodium quinoa seeds with SNP mitigated the adverse effect of salt stress on seed germination. In this regard, the amylase activity increased, which led to the starch degradation and a raise in the content of water-soluble sugars in seeds subjected to salt stress [216]. The effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the salt tolerance of plants can be phenomenologically similar to the effects of NO donors. Hence, NO and H2S donors had a similar positive effect on the salt tolerance of wild-type Arabidopsis plants, which was manifested in a decrease, under their influence, of water deficit in leaves, a decrease in oxidative damage, stabilization of membrane permeability, and chlorophyll content under the action of 175 mM NaCl [217]. Also, under the influence of NaHS and SNP treatment during salinity in Col-0 plants, the activity of antioxidant enzymes increased, but the stress-induced accumulation of proline declined.
There is information about the facilitation of seed germination as a result of treatment with a hydrogen sulfide donor under salt stress conditions (Table 2). An important hydrogen sulfide feature at salt stress is the triggering of a cascade that includes SOS proteins, which boosts the work of Na+/H+ antiporters and promotes the elimination of excess sodium from cytosol [69]. Treatment of alfalfa and cucumber plants, that had been subjected to salt stress, had a positive effect on ionic homeostasis (Table 2), increasing the K+/Na+ ratio in tissues [151, 219].
Carbon monoxide donors also raised the salt tolerance of plants. The germination of rice seeds during salinity was enhanced by treatment with exogenous carbon monoxide [220]. This treatment increased activity and expression of the Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD) gene, and also mitigated stress-induced oxidative damage. Treatment with a CO solution partially eliminated the effect of programmed cell death in the roots of wheat seedlings exposed to 200 mM NaCl [105]. Also, under the influence of exogenous CO, there was a significant increase in the expression of the Mn-SOD gene and stabilization of the total SOD activity under stressful conditions (Table 2). Notably, CO treatment also eliminated the stress-induced rise in NADPH oxidase activity.
It was shown that in wheat plants, under the salt stress, exogenous CO increased the expression of the Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase gene and weakened the expression of the proline dehydrogenase gene, which led to the accumulation of endogenous proline [237].
6.5. UV-B Irradiation
Amount of endogenous NO increases under various abiotic stresses, including UV-B irradiation [238]. It was previously found that one of the UV-B targets was microtubules [239, 240], which were directly involved in cell division, growth, and development of plants. Under the UV-B irradiation, reorganization and depolymerization of microtubules take place, which leads to disturbance of the cell’s functioning, morphological lesions in the main plant organs, and an inhibition of their growth. Moreover, cellular abnormalities can lead to programmed death of plant cells [240, 241]. To study the combined impact of NO on the growth and morphology of A. thaliana roots, as well as on the organization of microtubules in their cells, its intracellular content was changed by using a donor (SNP) and/or scavenger (cPTIO) and followed with subsequent UV-B irradiation. It was found that the pretreatment with 10 and 100 μM SNP leads to a partial restoration of the main roots growth, normal morphology of the epidermal cells of the transition and extension zone, as well as restoration of the original orientation of microtubules in the cells of these zones [239, 240].
Recently, a link has been established between NO and myo-inositol signaling, which may be involved in mediating UV-B-induced oxidative stress in plant cells [222]. Homozygous atips1 mutants of A. thaliana, deficient in inositol-3-phosphate synthase 1 (IPS1), a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of myo-inositol and its derivatives, were preliminarily treated with SNP at low concentrations (10, 100 μM) before UV-B irradiation led to a tissue-specific protective effect, most pronounced in the atips1 mutants. The obtained data indicate the existence of a functional relationship between changes in the NO content, the myo-inositol synthesis, and the organization of microtubules under the UV-B irradiation of plants. The effect of other gasotransmitters on the resistance of plants to UV-B radiation remains almost unexplored. There is evidence of a ROS-dependent increase in barley plant resistance to UV-B treatment with NaHS treatment (Table 2).
7. DONORS OF GASOTRANSMITTERS FOR EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH AND PRACTICAL USE
7.1. Nitric Oxide Donors
A large body of experimental data indicating the nitric oxide role in plant adaptation to abiotic stresses was obtained by treating plant objects with NO donors, and subsequent determination of resistance to a particular stress factor. There are more than 15 classes, including more than 300 compounds, known to be able to perform as NO donors [242, 243]. Their list is constantly expanding [243]. But compounds, that are most frequently used as NO donors, are nitroglycerin, diethylamine-NONOates, S-nitroso-N-acetyl-penicillamine, S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) [21, 34, 243].
It is SNP that is currently the most common NO donor, used both in research and in practice [23, 195, 222, 223, 244, 245]. In 1993, SNP-based medicines took the leading position among the emergency cardiovascular preparations based on nitric oxide donors, displacing almost entirely inorganic nitrites and largely organic compounds in the field of emergency medicine [246, 247]. The advantages of SNP in comparison with other NO donors are related to its stability, safety, low cost, solubility, permeability, a wide range of effective concentrations, and it has been well researched, etc. [243, 245]. However, it is not used for a prolonged therapeutic application, because of the numerous data on the likelihood of an increasing cyanides accumulation in liver and other organs, yielding for these purposes to organic donors of nitric oxide [245, 247, 248]. SNP belongs to photosensitive compounds and, being exposed to light, decomposes to release NO [249]. However, it is well known that in biological systems release of NO from SNP occurs in both non-enzymatic and enzymatic reactions in the presence of reducing agents (NADH, NADPH, thiols, and possibly ascorbate) [242] and/or membrane-bound enzymes (probably NADPH oxidase, etc...) [242, 250, 251].
To prove the physiological effect of SNP as a nitric oxide donor, and not as a complex compound, experiments are carried out using NO scavengers, which eliminate the physiological effects of SNP [34, 195, 223, 244] Sometimes, a so-called “depleted” SNP solution is used, which contains the products of SNP decomposition but not NO [21]. It is obtained by keeping the SNP solution in an open container in the light for several days. One of the disadvantages of SNP as a nitric oxide donor is the formation of cyanide during its decomposition, which can have a side effect on the physiological processes in plants [21].
Currently, there are no special preparations – NO donors – for use in crop production. There are only sporadic data on the use of nitric oxide donor SNP as a resistance inducer of agricultural plants in the field experiments [252]. Anyway, a significant pool of fundamental research data has been currently accumulated in the scientific literature featuring the possibility of utilising SNP to enhance plant resistance to the biotic and abiotic stresses [23, 253].
In addition to SNP, the so-called NONOates have recently become commercially available on the market. They consist of a diolate group [N(O-)N=O] linked to a primary or secondary amine, or to a polyamine via a nitrogen atom [254]. Spontaneously degrading at physiological pH and temperature, NONOates produce two NO molecules.
In some studies, on the induction of plant resistance to stresses, L-arginine [255] and nitrate [256] were used as NO sources. Recently, potassium and magnesium nitrates have been proposed to be used for seed priming [257]. In such case, their effects are, at least partially, associated with the action as sources of NO. Nevertheless, until now, SNP is used most often as a donor of nitric oxide for studies of the exogenous NO effect on the resistance of plants to the stresses.
7.2. Hydrogen Sulfide Donors
The term “hydrogen sulfide” means not only H2S as a dissolved gaseous compound but also the HS– anion, into which about 80% of the total molecular hydrogen sulfide is converted in physiologically normal conditions [87]. Most often, sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) is used as a donor of hydrogen sulfide and/or hydrosulfide anion. However, it has been shown that treatment of plants with this compound in sufficiently high concentrations causes a significant, but short-term, increase in the intracellular content of hydrogen sulfide [76]. For the biomedical research application, donors with a “milder” and prolonged action have been developed, which are now used in plant physiology too. One of those is a compound known as GYY4137 (morpholin-4-ium 4 methoxyphenyl(morpholino) phosphinodithionate) [258, 259]. It was found that treatment of Arabidopsis plants with GYY4137 caused a more prolonged increase in the H2S content in tissues compared to the action of sodium hydrosulfide [259]. Compounds that release H2S in certain intracellular compartments, for example, the AP39 molecule, which enters mainly mitochondria, are considered promising for use in agriculture [260]. Some works report about inorganic sodium polysulfides (Na2Sn, such as Na2S2, Na2S3, and Na2S4) as potential sources of hydrogen sulfide formation with a milder action, which can be converted to H2S in a biological environment [261]. However, the efficiency of such transformations depends on the pH of the medium and the corresponding pKa [262]. As an alternative to NaHS and other inorganic sulfur compounds, dialkyldithiophosphate has recently been proposed, which is able to slowly release H2S [263]. Treatment with this compound was shown to increase the weight of maize plants 4 weeks after the treatment by 39%. As already noted, nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide are in close functional interaction with each other and can mutually enhance the stress-protective effect on plants. In this regard, a donor of both NO and H2S named NOSH or NOSH-aspirin was recently synthesized [264]. It was shown that both of these preparations significantly increased the drought resistance of alfalfa, associated with an increase in the endogenous content of signaling molecules (NO and H2S) and an increase in antioxidant activity. However, the effectiveness of the preparation containing aspirin was estimated as higher [264].
7.3. Carbon Monoxide Donors
To the best of our knowledge, cases of a commercial use of carbon monoxide donors to enhance plant resistance to stresses have not been reported yet. However, CO donors have been used in experiments with animals since 1970 [265]. One of these is hematin, known as an HO1 inducer and CO donor. It was shown that after intravenous infusion of hematin-14C, rats produced equimolar amounts of labeled bilirubin and CO [266]. Another CO donor with a similar mechanism of action is hemin. In general, hematin and hemin are widely used in studies of the CO effects in animals and plants [93, 205, 265, 267].
Currently, a new generation of CO donors, of the CORM family, are used in human and animal physiology. CORM molecules are composed of carbonyl groups bonded to metals such as ruthenium or manganese. After the entry of such compounds into cells, a slow release of CO occurs due to ligand exchange reactions, and that pace of CO release minimizes toxic effects [268]. CORM compounds have recently been widely used in vivo in studies on animals or model cell systems [269, 270]. The effect of such CO donors on plants has not been properly studied yet. However, the extending of the range of available and non-toxic CO donors creates favorable prerequisites for their future application in crop production.
CONCLUSION
Currently, there are valid reasons to consider gasotransmitters as key players in plant cell signaling. These compounds are in close functional relationships with each other, as well as with such universal signaling mediators as calcium ions and ROS. GT do not have specific receptors. Their primary effects appear to be due to direct interaction with certain functional groups of proteins. Such interaction is an important kind of PTM (Fig. 3). In particular, for nitric oxide, such targets can be metal-containing groups that are nitrosylated, or tyrosine residues that undergo nitration, or thiol groups of cysteine that undergo S-nitrosation. The latter process, apparently, has the greatest regulatory potential due to its reversibility, as well as the possibility of competition with another process, persulfidation. The dominating of either persulfidation or S-nitrosation processes, probably, depends on the local concentrations of the corresponding GT in the cells, the redox potential, and other factors. Persulfidation is considered as a mechanism for regulating the functional activity of proteins (primarily enzymes), and as an effective way to protect proteins from oxidative damage (Fig. 3). In this regard, the enhancement of protein persulfidation can be considered as an adaptive process.
The action of carbon monoxide differs significantly from the PTMs caused by hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide since CO does not interact with thiol groups; in fact, its interaction with proteins is limited by the formation of coordination bonds with metals (primarily, binding to iron of heme-containing proteins) (Fig. 3). In this regard, a fairly wide range of CO biological effects remains a mystery.
The GT physiological effects are realized in close connection with ROS, calcium ions, and other mediators (Fig. 3). The molecular mechanisms of the functional interaction of GT and other mediators in plant cells remain largely unclear. Nevertheless, elimination of one or another mediator with the help of appropriate antagonists (inhibitors) very often eliminates the physiological effect of the compound under study.
It is likely that many connections in the “signaling web” account for the non-specificity of many of the effects of exogenous signaling mediators. Apparently, in this connection, activation of the same physiological reactions (primarily stress-protective ones) is possible by treating plants with various GT. There are numerous data on the ability of all three GT discussed in this review to enhance gene expression and increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes and reduce oxidative damage. Also, in many cases, GT enhances the accumulation of low-molecular-weight compounds with multifunctional protective effects (proline, glycine betaine, trehalose, etc..). The synthesis of stress proteins can also be enhanced in the presence of GT (Fig. 3).
The lack of confident knowledge on the molecular mechanisms of the GT physiological action hinders the development of theoretical foundations for their application in crop production. However, the accumulated extensive phenomenology of their stress-protective effects testifies to the very high potential of this group of physiologically active substances for their biological application. Their important advantage is the environmental safety. The data on the possibility of combined use of GT and plant hormones, involved in the delivery of the same protective reactions, are also increasingly accumulating. Usually, these combinations have synergistic effects [264, 271, 272], although, elaboration of this issue is beyond the remit of this review. The creation of stable and environmentally safe GT donors opens up broad prospects for their application in crop production, primarily as stress protectants.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
| GT | = Gasotransmitters |
| NO | = Nitrogen monoxide |
| CO | = Carbon monoxide |
| H2S | = Hydrogen sulfide |
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
FUNDING
None
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Dr. Yuriy Kolupaev is Exceutive Guest Editor of Journal The Open Agriculture Journal.
Dr. Аlla Yemets is Editorial Advisory Board of Journal The Open Agriculture Journal; Dr. Yaroslav Blume is EIC of Journal The Open Agriculture Journal.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge the suggestions of Dr. V. Kyrylenko (Institute of Food Biotechnology and Genomics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv) aimed to improve the language of the manuscript.


